Thermocol Composition: What Is Thermocol Made Of?

You're curious about thermocol, also known as expanded polystyrene foam? It's primarily made from polystyrene, a petroleum-derived plastic. Polystyrene starts as liquid styrene, which polymerizes and gains characteristics like lightweight, insulation, and moisture resistance. During production, tiny styrene beads are expanded using steam and a blowing agent, turning them into the familiar, feathery foam material. Despite its versatility, thermocol poses environmental challenges due to its non-biodegradable nature. This means recycling isn't straightforward. In everyday applications, thermocol is used for insulation, packaging, and crafts. Stick around to see how it's molded into so many useful forms.
Understanding Polystyrene
Polystyrene is a adaptable plastic that's integral to creating thermocol, also known as expanded polystyrene foam. When you investigate polystyrene properties, you'll find it's lightweight, durable, and resistant to moisture, which makes it an ideal material for different applications. Furthermore, polystyrene is derived from petroleum, making it a synthetic substance that poses environmental risks if not disposed of properly. The closed-cell structure of polystyrene gives it excellent insulating properties, allowing it to maintain temperature stability. It's also remarkably easy to mold, letting manufacturers create complex shapes and sizes, perfect for custom packaging solutions. You'll notice that polystyrene uses are extensive. It's commonly found in packaging materials, protecting everything from electronics to fragile items during shipping. Its shock-absorbent nature guarantees that products arrive safely at their destination. Besides packaging, polystyrene is widely used in the construction industry. It serves as insulation in walls, roofs, and foundations, contributing to energy-efficient buildings. In the food industry, you'll see it in disposable cutlery, cups, and containers due to its excellent thermal insulation properties. As a result, thermocol's applications extend across a range of sectors, showcasing its practicality and cost-effectiveness. With these attributes, polystyrene plays a significant role in multiple sectors, offering solutions that are both practical and cost-effective. By understanding its properties and uses, you can appreciate why it's a key component in thermocol production.
The Role of Styrene
Styrene serves as the building block for polystyrene, playing a vital role in creating thermocol. You might wonder how this small molecule contributes so considerably. Initially, let's look at styrene properties. It's a liquid hydrocarbon that can easily be polymerized to form polystyrene, the backbone of thermocol. This transformation is what gives thermocol its lightweight and insulating characteristics, making it ideal for packaging and construction.
However, it's not just about the properties; styrene safety is imperative too. When handling styrene, you should be aware of potential health risks. While it's generally safe once polymerized into polystyrene, inhaling or prolonged exposure to liquid styrene can lead to irritation or more severe health effects. It's vital to guarantee proper ventilation and protective equipment if you're working with styrene in its liquid form.
Knowing these aspects helps you appreciate the balance between utility and safety. Styrene's ability to morph into a versatile material like polystyrene is remarkable, but it requires careful handling to prevent any adverse effects. By understanding both its properties and safety measures, you can use styrene effectively and responsibly.
Expansion Process Explained

Understanding the properties and safety of styrene sets the stage for exploring how thermocol is actually created. You'll find that the expansion process is vital to transforming styrene into the lightweight material you know as thermocol. Initially, styrene beads are impregnated with a blowing agent, typically pentane, which assists in the expansion. When these beads are subjected to steam heat during pre-expansion, they soften and expand up to 50 times their original size. This transformation is fundamental, especially considering the material's greater strength and lower consumption compared to common adhesives.
Once pre-expanded, the beads undergo a stabilization period to allow for air to replace the pentane inside them, enhancing their foam properties. Now, using specialized expansion techniques, the beads are placed in a mold and reheated. This causes them to expand further and fuse together, forming a solid block of thermocol. The heat softens the beads just enough so they bond without leaving gaps, which is vital for achieving the material's unique insulation and cushioning properties.
You'll appreciate that this process not only gives thermocol its remarkable lightness but also its ability to be molded into different shapes and sizes for diverse applications. Mastering these expansion techniques is key to harnessing thermocol's full potential.
Environmental Considerations
With regard to environmental considerations, thermocol's impact is significant and multifaceted. As a consumer, you should be aware that thermocol, or expanded polystyrene, is not biodegradable, which poses a challenge for sustainability practices. Once disposed of, it can persist in landfills for hundreds of years, contributing to environmental pollution. However, there are steps you can take to minimize its impact.
Firstly, consider recycling methods available in your area. While traditional recycling facilities may not accept thermocol due to its lightweight nature and bulky volume, specialized programs do exist. These programs compact and process thermocol for reuse in items like picture frames or insulation materials. By participating in these initiatives, you're supporting efforts to reduce waste.
Additionally, you can investigate alternative materials that align better with sustainability practices. Biodegradable packing options or those made from recycled content can lessen your environmental footprint. When you must use thermocol, try to reuse it whenever possible, regardless of whether for storage, crafts, or shipping items.
Applications in Everyday Life
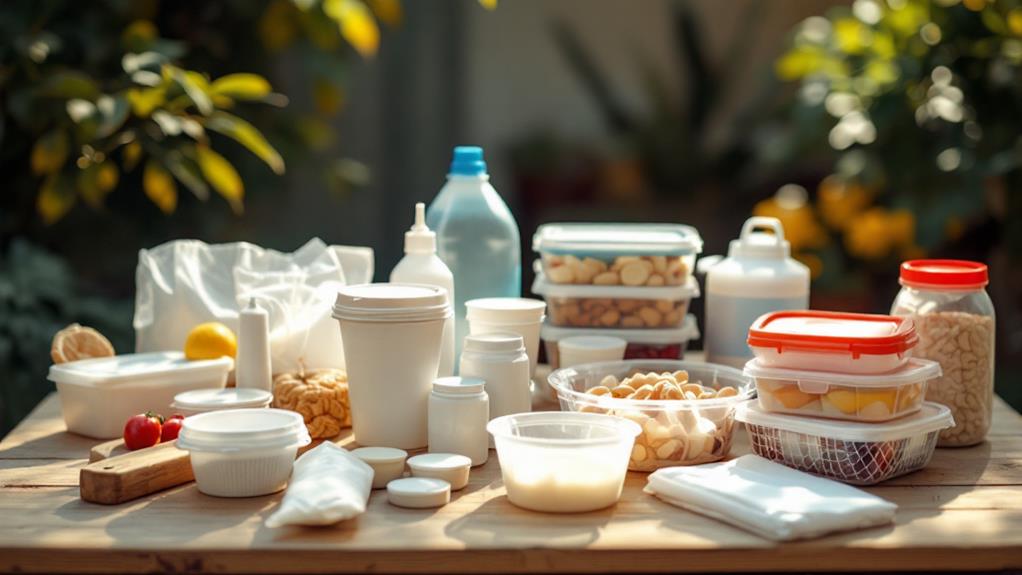

Many might not realize just how prevalent thermocol is in everyday life. You encounter it in different forms, from the moment you receive a package to when you insulate your home. As insulation materials, thermocol provides excellent thermal resistance, helping to maintain indoor temperatures efficiently. It's lightweight and easy to install, making it a popular choice for both temporary and permanent insulation needs. Regardless of whether you're insulating your attic or soundproofing a room, thermocol offers an effective solution.
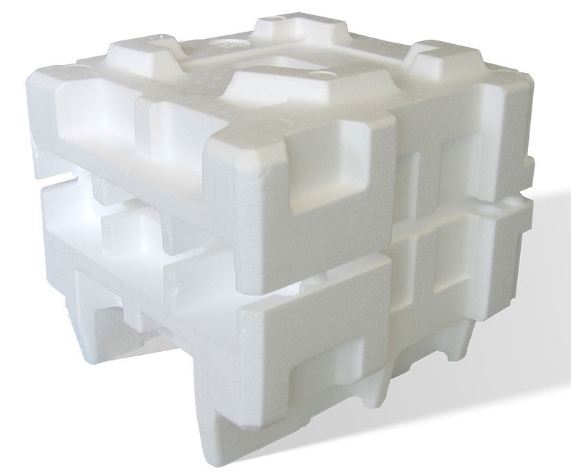
In packaging solutions, thermocol shines due to its cushioning properties. When you buy electronics, fragile items, or even food products, thermocol often plays an essential role in protecting these goods from damage during transit. It absorbs shocks and prevents breakage, ensuring your purchases arrive intact. You'll find it molded into specific shapes to snugly fit around products, providing maximum protection.
Moreover, thermocol is used in crafting, where its ease of cutting and shaping allows creative minds to bring ideas to life. From school projects to elaborate decorations, thermocol is a flexible material that supports a wide range of activities. So, next time you handle a package or tackle a home project, remember thermocol's invaluable role.