What Is Expanded Polystyrene?

You're likely familiar with expanded polystyrene (EPS), even if you don't realize it. EPS is a lightweight material made up of 95% air and 5% polystyrene, making it both cost-effective and versatile. It offers excellent thermal insulation and is perfect for protecting fragile items during shipping. Its resilience to moisture and pests guarantees durability, while its low weight makes for easy transport and installation. Industries ranging from packaging to construction rely on its affordability and strength. Curious about its manufacturing process or environmental impacts? There's a wealth of details waiting for you to uncover.
Characteristics of EPS
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) has become an everyday material thanks to its adaptable characteristics. You've likely encountered it in packaging, insulation, and numerous other applications. One of the standout features of EPS is its cost efficiency. It's an affordable option, making it a popular choice for industries looking to balance budget constraints with performance needs. With EPS, you get a material that's light on your wallet but heavy on benefits. Moreover, EPS is produced from polystyrene beads that are expanded through heating, resulting in a lightweight material with a unique structure that contains around 95% air and only 5% polystyrene, contributing to its low density and insulating properties the manufacturing process.
When it comes to material density, EPS offers a unique advantage. Despite being lightweight, it provides excellent strength and durability. This combination makes it ideal for shipping delicate items, as it can absorb impacts without adding significant weight. You'll find EPS in everything from coffee cups to building insulation, proving its adaptability across different sectors.
EPS's low material density also contributes to its excellent thermal insulation properties. You can count on it to maintain temperature, regardless of whether you're insulating a building or keeping your coffee hot. Moreover, its resistance to moisture and pests guarantees long-lasting performance. Overall, EPS stands out as a reliable, cost-effective solution with a remarkable range of applications, highlighting its indispensable role in modern industry.
Manufacturing Process
Creating Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) involves transforming small polystyrene beads into a versatile material through a fascinating process. You start with raw polystyrene beads, which are impregnated with a blowing agent. In the pre-expansion stage, you expose these beads to steam, causing them to expand up to 40 times their original size. This expansion is essential for achieving the lightweight nature of EPS, which makes it particularly valuable for applications like food packaging and handling that require effective insulation and protection.
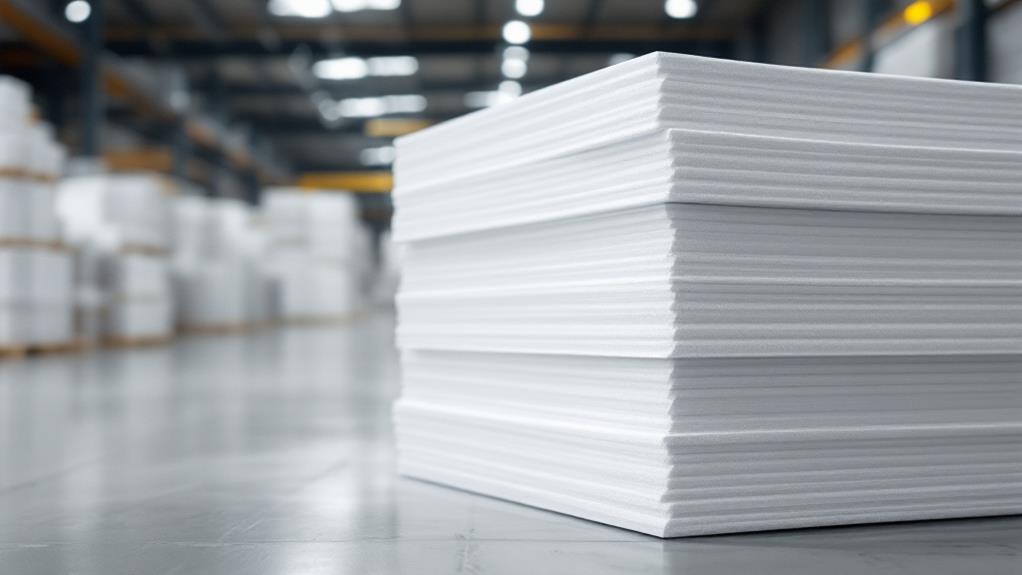
Once expanded, you move to the maturation process, allowing beads to stabilize and cool. Here, you ascertain quality control by checking for uniform bead size and density, which are crucial for the final product's performance. Next, you place the beads in molds, where they're again exposed to steam. This step fuses them into the desired shape, regardless of whether it's blocks, sheets, or other forms.
Throughout these production techniques, you must maintain stringent quality control. Regular checks guarantee that the beads are free of defects and meet specified standards. By managing temperature and pressure precisely, you achieve consistent quality in the EPS you're producing. This thorough process ensures that the final EPS product is ready for diverse applications, offering durability and reliability.
Common Applications
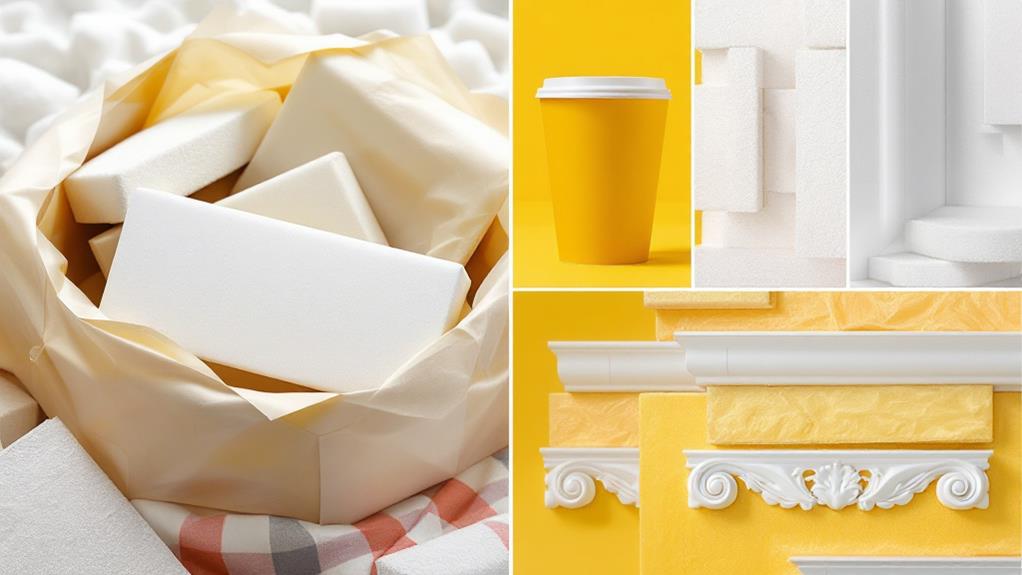

With regard to common applications of Expanded Polystyrene (EPS), its versatility and lightweight nature make it indispensable across multiple industries. You'll notice EPS often in packaging solutions because it provides excellent protection for fragile items during transit. Regardless of whether you're shipping electronics or delicate glassware, EPS acts as a cushion, absorbing impact and preventing damage. Its ability to be molded into different shapes means it can fit snugly around products, offering tailored protection that's hard to beat.
In construction, EPS is a favored material due to its durability and ease of use. You might find it as a component in construction materials like insulated concrete forms or structural insulated panels. These applications benefit from EPS's ability to maintain structural integrity while being easy to handle on-site. It's also used in geofoam, which is employed in civil engineering projects to reduce load on underlying soil and structures. This lightweight material makes transportation and installation quicker and more efficient, saving both time and costs.
Insulation Benefits
One of the standout benefits of using Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is its exceptional insulation properties. When you're looking to improve your building's thermal performance, EPS is a top choice. It provides excellent resistance to heat flow, which helps maintain a consistent indoor temperature. This means you won't need to rely as heavily on heating and cooling systems, enhancing your total energy efficiency. By cutting down on energy consumption, you not only save on utility bills but also contribute to a more sustainable environment.
Here are three reasons you should consider EPS for your insulation needs:
- Superior Thermal Insulation: EPS is renowned for its ability to trap air within its cellular structure, providing outstanding thermal performance. This makes it ideal for use in walls, roofs, and floors, keeping your home comfortable year-round.
- Cost-Effective: EPS offers an excellent balance between cost and performance. Its energy efficiency translates to lower heating and cooling expenses, making it a smart investment in the long run.
- Durability and Moisture Resistance: EPS is resistant to moisture and doesn't degrade over time, ensuring that its insulating properties remain effective for the lifespan of your building.
Environmental Impact
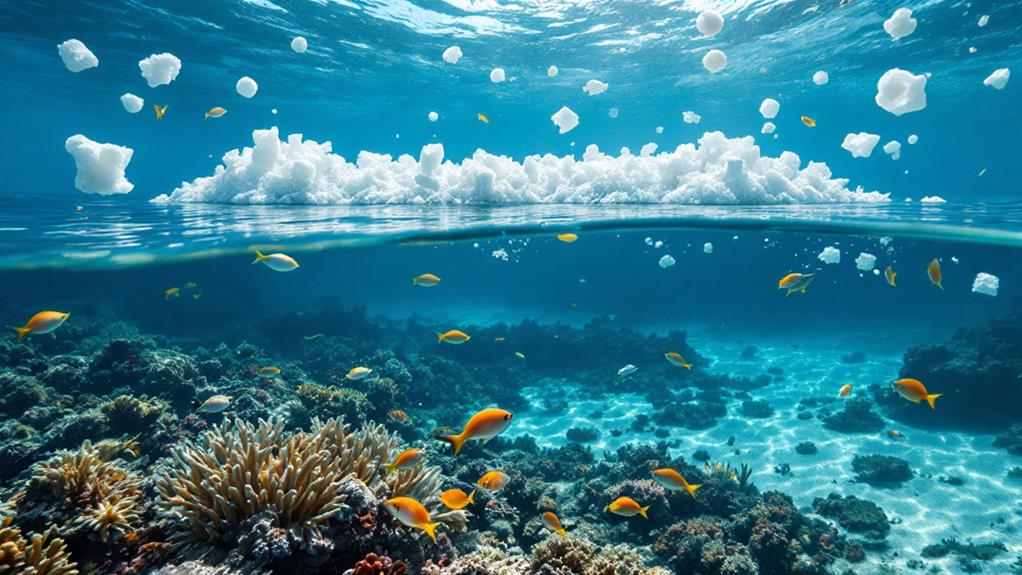

While EPS offers significant insulation benefits, it is vital to evaluate its environmental impact. You might already know that EPS, or expanded polystyrene, presents several environmental challenges. One of the primary issues is its recycling challenges. EPS is light and bulky, making it difficult and costly to transport for recycling. Many recycling facilities don't accept EPS because it requires specialized processes that aren't always available or economically viable. This means a lot of EPS ends up in landfills, where it takes up space without breaking down efficiently.
Moreover, biodegradability concerns are significant when considering EPS's environmental footprint. EPS doesn't biodegrade easily—if at all—in natural environments. This means it can persist for hundreds of years, contributing to long-term pollution in landfills and potentially entering waterways, where it breaks into smaller particles. These microplastics can harm marine life and ecosystems, leading to broader environmental issues.
You should also consider how EPS, when improperly disposed of, can release toxic substances into the air and soil, posing risks to both human and environmental health. It is imperative to weigh these factors when choosing materials for your projects or making decisions about disposal.
Future Innovations
Looking ahead, technological advancements hold promise for tackling the challenges associated with expanded polystyrene (EPS). As you investigate future innovations, you'll find exciting developments that could reshape how EPS is used and disposed of. Imagine a world where EPS integrates with smart packaging technologies, allowing you to track and monitor the conditions of the packaged goods. This innovation could revolutionize industries by ensuring product quality and reducing waste.
Furthermore, researchers are examining biodegradable alternatives to traditional EPS, aiming to create materials that maintain the same protective qualities but break down more easily in the environment. This shift could greatly reduce the ecological footprint of packaging materials.
Here are three remarkable future innovations to watch:
- Nanotechnology Integration: By improving EPS with nanomaterials, it's possible to increase its durability and reduce raw material usage, making it more sustainable.
- Recycling Enhancements: New chemical recycling methods could allow EPS to be broken down into its core components, making it easier to recycle and reuse.
- Biodegradable EPS: Scientists are working on creating EPS that biodegrades naturally, providing an eco-friendly alternative without sacrificing performance.
These innovations aim to balance efficiency, sustainability, and environmental responsibility.