What Is Polystyrene Foam?

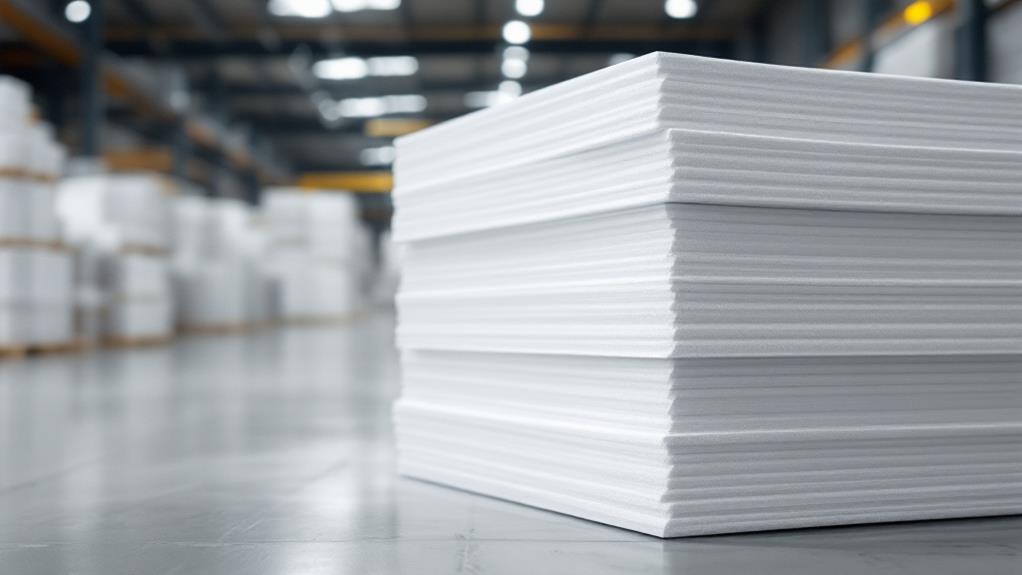
You know polystyrene foam from products like Styrofoam, a lightweight, rigid material that excels in packaging and insulation. Made from polystyrene polymer, it consists of long styrene chains forming a solid network filled with air, creating excellent thermal insulation and shock absorption. Manufacturing involves expanding tiny beads with steam and molding them into sheets or blocks. It's widely used to keep takeout food warm and protect fragile items during shipping. Despite its benefits, it's not biodegradable, posing environmental concerns. Choosing biodegradable options or learning about recycling can help you make more sustainable decisions. There's more to uncover about this material's impact and alternatives.
Composition and Structure
How exactly is polystyrene foam composed? When you explore the molecular structure, you'll find it's made up of long chains of styrene monomers. These monomers bond together to form a solid polymer, which is a type of polymer produced from natural products or synthesized. The structure is fundamentally a network that's filled with air, giving polystyrene its lightweight and insulating characteristics. In this matrix, the polymer properties are significant. They endow the foam with its strength and flexibility, despite the foam's low density.
Polystyrene itself is a polymer that's derived from the monomer styrene, a liquid hydrocarbon. When polymerized, it forms a rigid and transparent plastic. However, when expanded into foam, air gets trapped within the structure, which is why polystyrene foam feels so light. The polymer properties, such as resistance to moisture and chemicals, make it adaptable for differing applications.
You'll notice that in its foam state, polystyrene maintains its insulating capabilities, which is why it's commonly used in products like coffee cups and packaging materials. Its molecular structure and inherent polymer properties make it an ideal material for situations where lightweight and insulation are vital.
Manufacturing Process
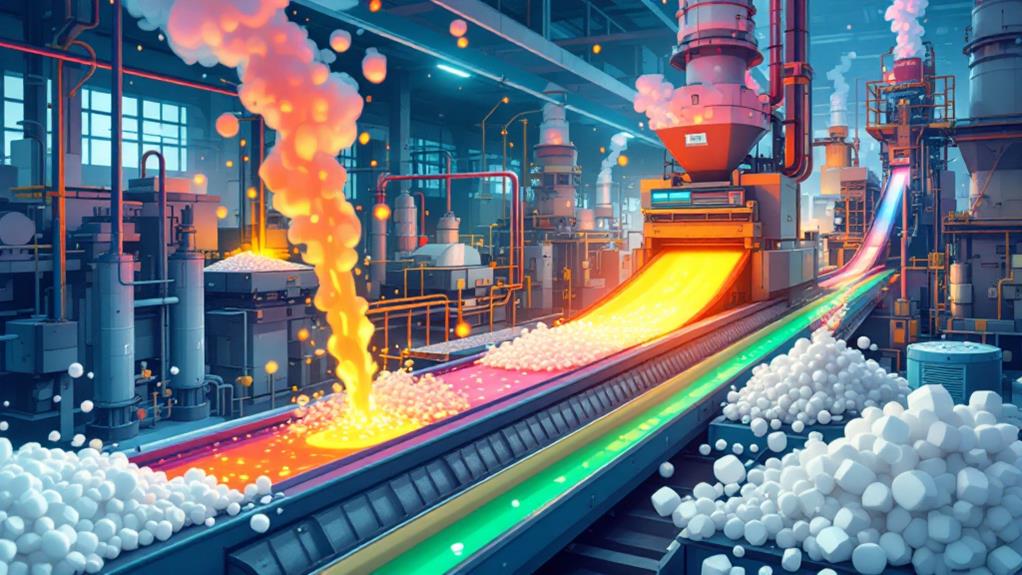
The creation of polystyrene foam involves a fascinating interplay of chemistry and engineering. To start, you'll need to understand the production methods that transform solid polystyrene into the lightweight foam you see every day. It all begins with tiny beads of polystyrene, which are expanded using steam. This process increases their size dramatically, making them light and airy. Particularly, these polystyrene beads are produced from hydrocarbon materials derived from petroleum, comprising styrene and benzene molecules, which highlights their synthetic nature and manufacturing process. Once expanded, the beads are molded into larger blocks or sheets through a combination of heat and pressure.
The foam characteristics depend heavily on these production methods. By adjusting the amount of steam and pressure, manufacturers can control the density and strength of the final product. This flexibility allows for a wide range of applications, from insulative panels to disposable cups.
Consider the emotions and marvel at the:
- Transformation: From solid beads to lightweight foam.
- Innovation: Ingenious methods to create diverse characteristics.
- Precision: Exact control over density and strength.
- Efficiency: Maximizing material use with minimal waste.
- Sustainability: Efforts to recycle and reduce environmental impact.
These steps not only highlight the complexity of the manufacturing process but also demonstrate how integral this material is to modern life.
Common Applications

In everyday life, you'll find polystyrene foam in a surprising variety of places. It's a go-to material for packaging solutions due to its lightweight and protective qualities. When you order something fragile online, chances are it's cushioned by polystyrene foam. Its shock-absorbing properties make it ideal for safeguarding electronics, glassware, and other breakables during transit. You'll often spot it in the form of packing peanuts or molded inserts, ensuring your purchases reach you intact.
Polystyrene foam also plays a significant role in the food industry. You've probably encountered it as food containers, especially for takeout meals. Its insulating properties (without diving into too much detail here) help keep your hot foods hot and cold foods cold. Those coffee cups you grab on the go? Often made from polystyrene foam to maintain your drink's temperature while keeping your hands comfortable. It's also a staple at grocery stores for packaging foods like meats and produce.
Beyond packaging and food containers, polystyrene foam is used in arts and crafts, event decorations, and even stage props. Its versatility offers creative possibilities, making it a favorite material for DIY projects and professional settings alike.
Insulating Properties
Polystyrene foam stands out for its exceptional insulating properties, making it a favorite in multiple industries. As you investigate its benefits, you'll uncover how it improves thermal efficiency, ensuring your home or business maintains the desired temperature without excessive energy use. This means significant energy savings while keeping your environment comfortable. Imagine reducing your energy bills as the foam traps heat in the winter and keeps it out during the summer.
Here's why polystyrene foam's insulating properties should matter to you:
- Cozy Comfort: Enjoy a consistent indoor climate, free from annoying drafts and temperature fluctuations.
- Lower Bills: Experience tangible energy savings as your heating and cooling systems work less hard.
- Eco-Friendly Efforts: Contribute to a greener planet by consuming less energy.
- Peace of Mind: Rest easy knowing your insulation is working efficiently, protecting your investment.
- Sound Barrier: Relish a quieter environment as the foam helps reduce noise penetration.
Environmental Impact
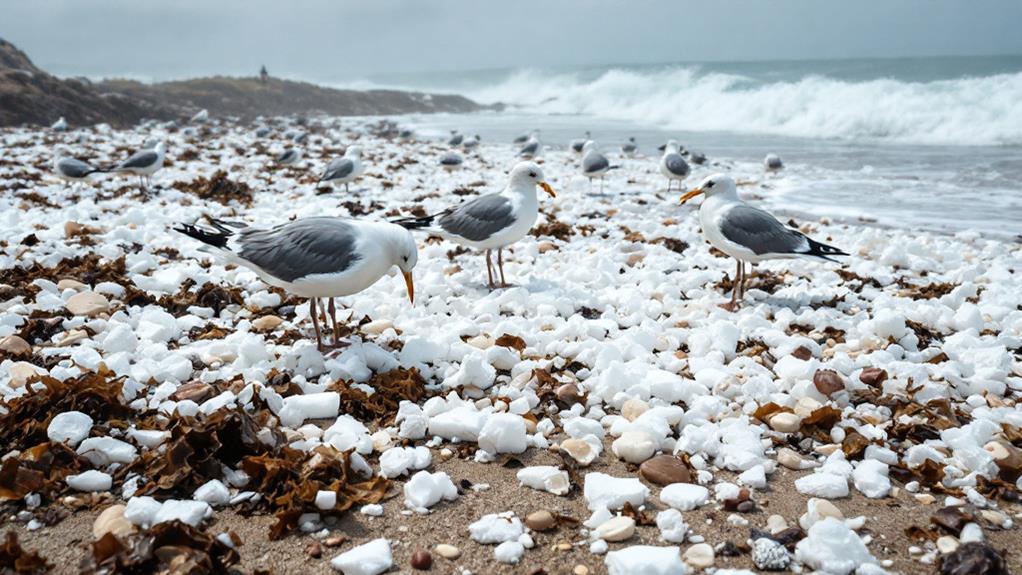

While enjoying the energy-saving benefits of polystyrene foam, it is crucial to reflect on its environmental impact. This material, commonly used in packaging and insulation, raises significant environmental concerns. Since polystyrene foam is non-biodegradable, it persists in the environment for hundreds of years, contributing to the growing global waste problem. When improperly disposed of, it often finds its way into waterways and oceans, posing a threat to marine life.
The wildlife impact is particularly alarming. Animals, mistaking polystyrene for food, can ingest it, leading to blockages, malnutrition, or even death. This disrupts food chains and harms biodiversity. Moreover, polystyrene foam can break into smaller pieces, called microplastics, which are nearly impossible to clean up and can enter the food web, affecting both wildlife and potentially human health.
Furthermore, the production process of polystyrene foam emits harmful pollutants and greenhouse gases, contributing to air pollution and climate change. These environmental concerns compel us to think critically about our reliance on this material. By understanding these impacts, you can make more informed choices and advocate for responsible usage and disposal of polystyrene foam products.
Recycling and Alternatives
As awareness of environmental issues grows, many people are seeking ways to recycle polystyrene foam and explore sustainable alternatives. However, recycling challenges abound because polystyrene foam is bulky and lightweight, making it costly to transport and process. Not every recycling facility accepts it, so you might have to search for specialized locations.
Considering biodegradable options can help reduce your environmental footprint. These alternatives break down naturally, minimizing harm to the planet. For example, biodegradable packing peanuts made from cornstarch dissolve in water, providing a guilt-free way to ship items.
When considering alternatives or recycling, keep these emotional points in mind:
- Hope: Every little bit of effort counts in protecting our planet.
- Frustration: The complexity of recycling polystyrene foam can feel overwhelming.
- Inspiration: Uncovering groundbreaking biodegradable options can spark creativity.
- Urgency: Our planet needs immediate action to reduce plastic waste.
- Empowerment: You have the power to make conscious choices for a sustainable future.