What Is Styrofoam Made Of?

Styrofoam is made from polystyrene, a flexible plastic that offers lightness and insulation. During manufacturing, polystyrene beads are expanded with steam and pressure, incorporating air to create foam. This process gives Styrofoam excellent thermal and moisture-resistant properties. It's widely used for packaging, insulation, and even disposable items like cutlery due to durability. However, its environmental impact is significant because it's not biodegradable and recycling is challenging. Understanding how polystyrene transforms through this efficient process into a material that's both incredibly useful and environmentally controversial might surprise you further.
Composition of Styrofoam
Consisting primarily of polystyrene, Styrofoam is a lightweight material that's been a staple in packaging and insulation. Its remarkable qualities make it widely used for food packaging and handling, preventing spoilage of perishable goods like meat and fish. You might not realize it, but the composition of Styrofoam isn't just about its core material. It's also about how it's manufactured and what happens after its use. The manufacturing techniques involve expanding polystyrene beads using steam and pressure, which creates a foam structure. This process makes Styrofoam incredibly lightweight and gives it excellent thermal insulation properties. It's fascinating how these tiny beads undergo such a transformation to become the foam products you're familiar with.
But what about after you've used Styrofoam? Recycling methods for Styrofoam are evolving, though they can be quite challenging. The material's lightweight nature makes it economically unviable to transport for recycling in many cases. However, some groundbreaking techniques are emerging. Densification involves compressing the foam to reduce its volume, making it easier to transport and recycle. Chemical recycling methods are also under development, aiming to break down Styrofoam into its original components for reuse. By understanding these processes, you can appreciate both the utility and the environmental challenges associated with Styrofoam's composition.
Polystyrene: The Core Element
At the heart of Styrofoam's composition lies polystyrene, a versatile plastic that's vital to its structure and functionality. When you look at polystyrene, you're seeing a material that's widely used due to its lightweight and insulative properties. It starts with polystyrene production, where styrene monomers are polymerized to create longer chains, resulting in polystyrene beads. These beads are then used in diverse applications, including packaging, insulation, and even in the production of disposable cutlery and plates. Similar to how yeast transforms dough into spongy bread through fermentation, polystyrene's unique properties make it fundamental in many everyday products, including those that require durability and insulation such as spongy bread.
You're probably familiar with polystyrene applications in everyday life. Think about the coffee cup that keeps your drink warm or the packaging that cushions electronics during shipping. Polystyrene excels in these roles because it's durable yet lightweight, making it easy to handle and transport. It also offers impressive resistance to moisture, which is why it's often chosen for insulating buildings.
Understanding polystyrene's role in Styrofoam helps you appreciate its widespread usage. Whether it's protecting fragile items or keeping your beverages at the right temperature, polystyrene is the unsung hero behind Styrofoam's effectiveness. As you've now seen, polystyrene is the core element that makes Styrofoam so indispensable in varied industries.
The Expansion Process

To truly understand Styrofoam, you need to investigate the expansion process, a fascinating transformation that turns tiny polystyrene beads into the familiar foam. Initially, these beads are subjected to steam, causing them to expand considerably. This is because each bead contains a blowing agent, typically pentane, that vaporizes under heat, inflating the beads like miniature balloons. This initial step in expansion techniques is essential, as it sets the stage for the foam's eventual structure and density.
After the beads have expanded, they undergo a stabilization period to cool down and release any trapped gases. This step guarantees that the beads maintain their newly acquired size and shape. Next, the beads are fed into molds where they're subjected to another round of steam. This heat causes the beads to fuse together, solidifying into a single piece of Styrofoam. The fusion process determines the foam density, which is critical for its insulating properties and structural integrity.
Properties and Characteristics
Understanding the properties and characteristics of Styrofoam reveals why it's such a flexible material. When you look closely at Styrofoam, you'll notice it's impressively lightweight yet strong enough to hold its shape. This is due to its structure, which consists of 98% air. The air pockets within Styrofoam make it an excellent thermal insulator. Regardless of you're using it to keep your drinks cold or your home warm, Styrofoam's thermal insulation capabilities are hard to beat. It effectively reduces heat transfer, keeping temperatures stable in different environments.
Another standout feature is its ability to absorb sound. This property makes Styrofoam a popular choice in construction and packaging industries, where sound absorption can be essential. By reducing noise levels, it improves the acoustics of a room or protects delicate items during transit. Moreover, Styrofoam is water-resistant, which contributes to its durability. It doesn't absorb moisture, making it suitable for damp or wet conditions.
You'll find Styrofoam easy to cut and shape, allowing for a range of applications and designs. Its resilience under pressure and flexibility in use make it a go-to material across multiple industries. From building insulation to soundproofing solutions, Styrofoam's characteristics guarantee it performs effectively.
Environmental Impact
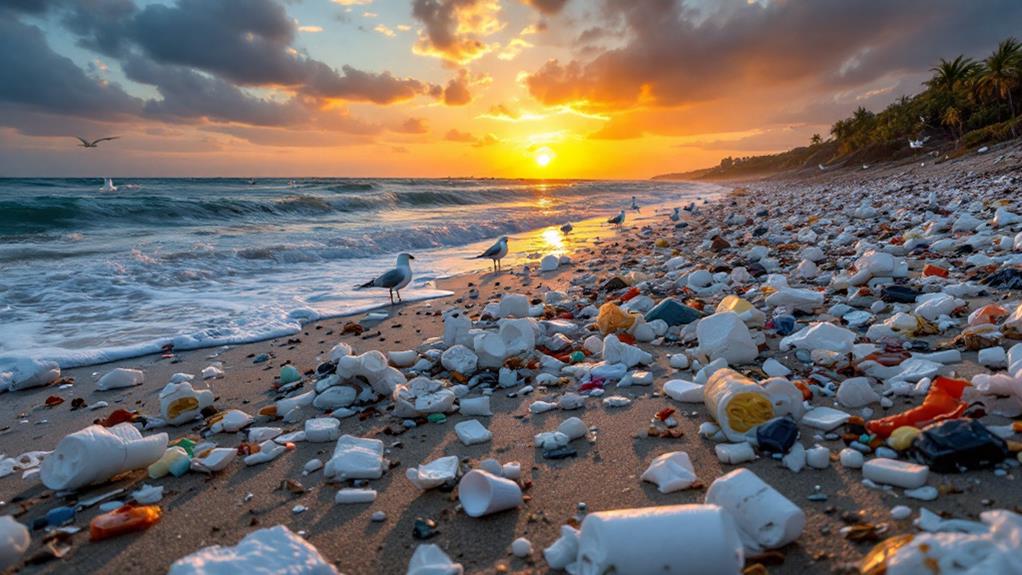

Many are concerned about the environmental impact of Styrofoam. As a consumer, you might not realize how much this material contributes to pollution and environmental degradation. Styrofoam, technically known as expanded polystyrene (EPS), is resistant to breaking down. This means it can persist in the environment for hundreds of years, posing threats to wildlife and ecosystems. Animals often mistake Styrofoam pieces for food, leading to ingestion and, ultimately, harm or death.
One of the significant issues with Styrofoam is the recycling challenges it presents. While recycling programs exist, they're not widespread or efficient. Styrofoam is bulky and lightweight, making it costly to transport and process. Many recycling centers simply don't accept it due to these logistical hurdles. As a result, vast amounts end up in landfills where they occupy space and potentially leach harmful chemicals into the soil and water.