What Is the Difference Between Xps and Eps Foam?
When you compare XPS and EPS foam, the differences start with their structures and manufacturing processes. XPS foam is extruded, creating a denser, closed-cell structure that offers superior moisture resistance and durability. EPS foam is made by expanding beads, forming a lighter, open-cell structure that's more budget-friendly but susceptible to water absorption. XPS provides better thermal insulation, making it ideal for space-constrained applications, while EPS suits projects needing thicker insulation on a tighter budget. XPS is more robust and lasts longer but costs more. There's much more to investigate about their applications and environmental impacts.
Manufacturing Process
The intricacies of manufacturing processes can greatly impact the properties of materials like XPS and EPS foam. When you explore the foam types, you'll see significant differences in their production methods. XPS, or Extruded Polystyrene Foam, is made by melting together polystyrene crystals with different additives. This mixture is then extruded through a die, forming a closed-cell structure. This method guarantees uniformity and results in a dense, strong, and moisture-resistant foam. The continuous extrusion process means XPS often comes in sheets, providing consistent quality and performance. Furthermore, the properties of the foam can be influenced by factors such as temperature and pressure during manufacturing, much like how yeast activity affects bread texture and volume.
On the other hand, EPS, or Expanded Polystyrene Foam, involves a completely different approach. EPS is produced by expanding small polystyrene beads using steam. The beads are then molded into blocks or sheets. This process creates a foam with an open-cell structure, making it lighter and less dense than XPS. The individual beads are visible, and the foam can be more susceptible to water absorption and mechanical damage.
Understanding these production methods is vital because they influence the foam's application and performance. By knowing how XPS and EPS are made, you can better decide which foam type suits your specific needs.
Thermal Insulation Properties
When comparing the thermal insulation properties of XPS and EPS foam, you'll notice distinct differences that could influence your choice. XPS foam generally offers lower thermal conductivity compared to EPS. This means XPS provides better insulation efficiency, which is essential if you're aiming to enhance energy savings. With lower thermal conductivity, XPS can offer the same level of insulation with a thinner layer, making it a space-efficient option for different applications. Furthermore, just as sleep deprivation can greatly impair cognitive functions, the choice of insulation material can profoundly affect the overall performance of a building sleep deprivation's consequences.
On the other hand, EPS foam can still be a viable choice, especially if budget constraints are a concern. While EPS has a higher thermal conductivity than XPS, it can still provide adequate insulation efficiency for many projects. It's vital to assess your specific insulation needs and how much you're willing to invest in thermal performance.
Consider how the insulation efficiency of each type affects your overall project goals. If you require a high-performing insulation material and space is limited, XPS might be the better choice. However, if your project can accommodate a thicker layer of insulation and you need to stick to a tighter budget, EPS could meet your requirements while still providing decent thermal insulation properties.
Moisture Resistance
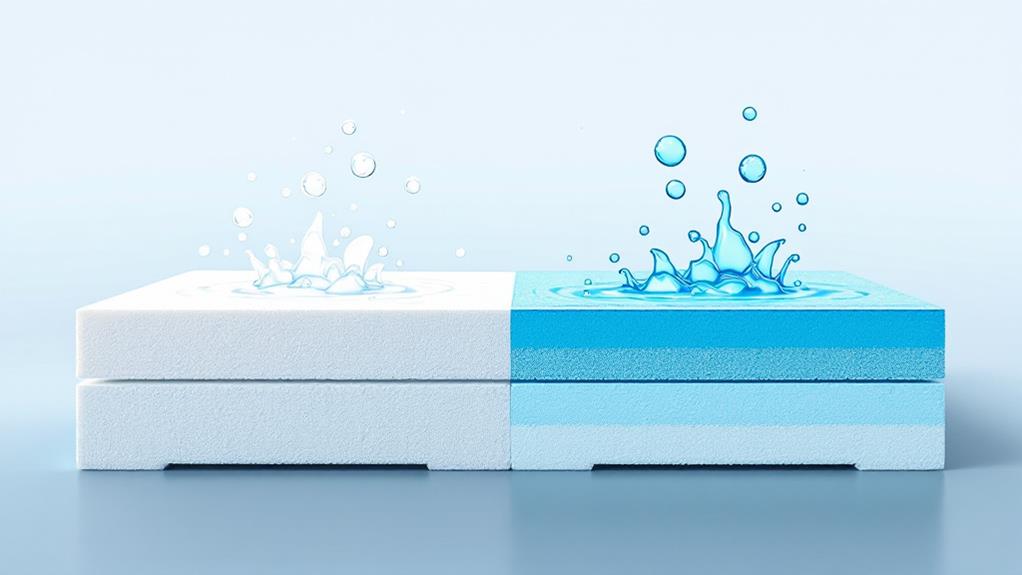

With moisture resistance being a crucial factor in selecting insulation materials, understanding the differences between XPS and EPS foam is essential. Regarding moisture absorption, XPS (extruded polystyrene) foam outperforms EPS (expanded polystyrene) foam. XPS is designed with a closed-cell structure, which considerably reduces the amount of moisture it can absorb. This makes XPS an excellent choice if you're looking for insulation in areas prone to high humidity or direct contact with water, like basements or below-grade applications.
EPS foam, on the other hand, has an open-cell structure, which makes it more susceptible to moisture absorption. While it still offers a degree of moisture resistance, EPS is less effective as a moisture barrier compared to XPS. This can potentially lead to decreased insulating performance over time if the foam becomes saturated.
When considering barrier effectiveness, XPS provides a more reliable shield against water infiltration. It helps maintain its insulating properties and structural integrity despite exposure to damp conditions. So, if moisture resistance is a top priority for your project, opting for XPS foam could be the smarter choice to guarantee lasting performance and protection.
Durability and Strength
Considering durability and strength, XPS foam typically comes out on top compared to EPS. When you're choosing between XPS and EPS foam for your project, understanding their differences in compression resistance and load capacity is essential. XPS foam is known for its higher compression resistance, making it a more robust option for applications where you expect heavy loads or pressure. This characteristic means XPS can withstand more force without deforming, which is especially significant for construction projects or insulation tasks that demand stability.
Here's why you might prefer XPS over EPS regarding durability and strength:
- Compression Resistance: XPS offers superior compression resistance, guaranteeing it maintains its shape and performance under stress. If you anticipate your foam needing to support weight or endure significant pressure, XPS is the better choice.
- Load Capacity: Thanks to its denser structure, XPS has a higher load capacity than EPS. This makes it ideal for supporting heavy objects or being used in structural applications.
- Longevity: XPS tends to last longer due to its durability, offering a more reliable long-term solution. You won't need to worry about frequent replacements or repairs, which is a big plus.
Choosing wisely guarantees you get the most out of your foam investment.
Cost Comparison

Cost often plays a significant role in deciding between XPS and EPS foam for your project. When considering price trends, EPS foam generally comes out as the more budget-friendly option. This is primarily due to its manufacturing process, which is less complex and less resource-intensive than that of XPS foam. EPS is widely available in the market, making it easier to find at competitive prices, especially if you're dealing with a tight budget.
XPS foam, on the other hand, tends to be more expensive. Its higher price tag can be attributed to its denser structure and superior insulating properties, which may justify the cost depending on your project's requirements. If you're looking for better thermal resistance and moisture control, the supplementary expense of XPS might be worthwhile.
Market availability can influence your decision as well. While EPS is usually more accessible regarding quantity and variety, XPS might be limited by specific market demands or regional availability. It's essential to assess these factors when planning your project, as they can impact both short-term costs and long-term savings. By weighing both price trends and market availability, you can make an informed choice that aligns with your budget and performance needs.
Environmental Impact
Although both XPS and EPS foam have their uses, their environmental impacts differ markedly. If you're considering which one to choose based on sustainability practices, it's crucial to weigh their differences. XPS (extruded polystyrene) foam is known for its closed-cell structure, which makes it less permeable to moisture. However, it often uses a blowing agent with higher global warming potential. On the other hand, EPS (expanded polystyrene) foam, with its open-cell structure, is generally considered to have a lesser environmental footprint due to its less harmful manufacturing process.
When it comes to recycling options, EPS foam has the upper hand. Here's why:
- Recyclability: EPS is 100% recyclable, and many curbside recycling programs accept it, making it easy for you to dispose of responsibly.
- Reuse: EPS can be repurposed into products like picture frames or insulation beads, contributing to a circular economy.
- Waste Reduction: EPS foam's lightweight nature means less waste volume, reducing landfill impact.
Installation and Handling

When selecting between XPS and EPS foam based on installation and handling, you'll find that each has its own set of characteristics that affect ease of use. XPS foam is denser and more rigid, making it relatively easy to cut with a utility knife or hot wire cutter. This allows for precise cutting techniques, ensuring a snug fit in different applications. On the other hand, EPS foam is lighter and can be cut using basic tools like a handsaw or even a kitchen knife, though it may not offer the same level of precision as XPS.
Handling these foams requires some storage precautions to maintain their integrity. XPS foam is more resistant to moisture, so it can be stored in a wider range of environments without significant risk of degradation. EPS foam, however, is more susceptible to moisture and should be kept in a dry, covered area to prevent water absorption and potential damage.
Both foams are lightweight, making them easy to maneuver during installation. However, due to its higher density, XPS might feel slightly heavier than EPS. Ultimately, your choice may depend on the specific demands of your project and your comfort with the required handling techniques.
Best Applications
XPS and EPS foam each shine in specific applications due to their unique properties. When you're deciding between the two, consider the design considerations and performance factors that best suit your project needs. XPS foam, known for its durability and moisture resistance, is a top choice for applications where water exposure is a concern. It's ideal for below-grade insulation, such as foundation walls and slab foundations, where its moisture-resistant properties prevent water infiltration and maintain thermal performance.
Here are three best applications for each:
XPS Foam:
- Foundation Insulation: Its moisture resistance makes it perfect for insulating basement walls.
- Roof Insulation: Offers excellent compressive strength, making it suitable for flat roofs.
- Wall Sheathing: Provides a continuous insulation layer, enhancing thermal efficiency.
EPS Foam:
- Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs): Lightweight and easy to handle, EPS is great for SIPs, offering high thermal resistance.
- Exterior Insulation and Finish Systems (EIFS): Its versatility and cost-effectiveness make it a popular choice for EIFS.
- Packaging and Shipping: EPS's shock-absorbing properties protect fragile items during transport.